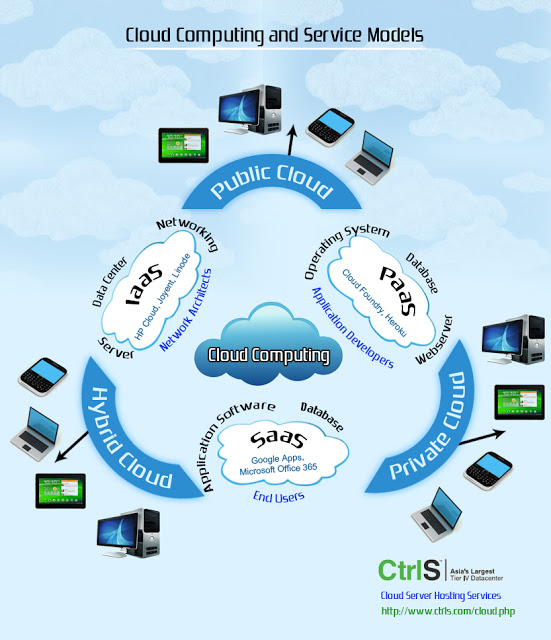
The cloud computing infrastructures that are set up on servers with contrasting stratum of virtualization technologies and contain dependable services; are distributed through data centers. These services are available at any place where provision for access to the network is found. The most commonly described cloud computing infrastructures are public, private and hybrid clouds, although there is one more know as community cloud.
Public clouds are generally available over the Internet while private clouds can be found at establishments of organizations. Private clouds can also be located at a co-location facility and can be made available over the Internet. Hybrid clouds combine both public and private cloud models and provide scalability from third party cloud providers or when an organization requires it.
Public Cloud Infrastructure
In most cases, public clouds are hosted away from customer premises and can be made available to third parties with applications combined together from different customers over the network and storage systems, i.e. through cloud servers. They assist in the reduction of costs and customer risks by supplying an adjustable broadening to business infrastructure. The availability of other applications that are operating in the cloud should be transparent to end users and cloud designers when a public cloud is put into operation with data locality, security and performance in mind.
Private Cloud Infrastructure
Private clouds are available to provide the control over quality of service, security and data, built for the use of one client. These clouds can be redistributed in an enterprise data center and may also be redistributed at a compilation place. Infrastructures for private clouds can be administered and constructed by a cloud provider or by a company’s own IT organization. With the hosted private archetype, a company can operate, set up and establish the infrastructure to hold up a private cloud inside a company’s enterprise data center.
Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Hybrid clouds are an amalgamation of public and private cloud models. They assist in the provision of on demand externally provisioned scale. A private cloud with the resources of a public cloud can be used for the maintenance of service levels in the very fast workload variations. A hybrid cloud can also be for the handling of spikes of workload that has been contemplated and prepared in advance. This is known as surge computing and a public cloud can be applied for the operations of chores that can be redistributed easily on a public cloud.
Hybrid clouds decide how to redeploy operations over both private clouds and public clouds. If the operation is without identity, or the information is small, a hybrid cloud will probably be much more favorable compared to when large amounts of data are transferred into a public cloud for small amounts of processing.
Cloud infrastructure is vital to cloud hosting and the advantages of this means of hosting make it a very attractive alternative for any size of business that requires changeable, dependable and high performing hosting solutions. There is however no concrete and authoritative answers to cloud computing infrastructure model that ought to be used and everything really depends on the location of the network and the type of data processing being carried out. With situations being unique, organizations must consider the advantages and disadvantages of each cloud infrastructure model as well as their technical, legal and business requirements.